1. Introduction
Ginkgo biloba has extensive biological activities and contains a variety of chemical composition such as flavonoids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, phenols, organic acids, alkaloids, amino acids, steroidal compounds, trace elements, etc. Among them, vitamin C, vitamin E, carotene and calcium, phosphorus, boron, selenium and other mineral elements are abundant, but the most important medicinal value components are flavonoids and terpenoids. Flavonoids and terpenoids have many functions like vascular dilation and anti-oxidant.
Ginkgo Biloba Extract (GBE), which refers to the effective substance extracted from Ginkgo Biloba, contains Ginkgo flavonoids, ginkgolides and other substances, which can dilate blood vessels, protect vascular endothelial tissue and low density lipoprotein, regulate blood lipid, inhibit PAF (platelet activation factor) and thrombus formation and scavenge free radicals and so on. Many clinical studies have shown that standardized ginkgo leaf extract can significantly reduce patients' mental illness like alzheimer's disease.

Natural products are often thought to be natural to correct and improve people's health systems. Unfortunately, the competitive atmosphere leads to the emergence of fake products in the final market. The active components in ginkgo biloba extract are flavonoid glycosides and terpenoids whose content in ginkgo standard extract is greater than 24% and 6% respectively. At present ordinary analytical methods have hydrolysis step. This hydrolysis process converts flavonoids into aglucone that do not exist in ginkgo, while many of these aglucone such as quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin are adopted for the quality control of ginkgo biloba products, so the quality of these inappropriate control index provides an opportunity to the adulteration of ginkgo biloba extract.
The pharmacopoeia provides some sophisticated analytical methods for standardized plant products, including raw materials, extracts and final plant products. In the case of ginkgo biloba, USP(United States Pharmacopeia), BP(British Pharmacopoeia), EP(European Pharmacopoeia) and CP(Chinese pharmacopoeia) all have their own testing methods, which required the content of ginkgo flavonoids to be between 22.0% and 27.0%. But for the hydrolyzed ginkgo biloba samples, their respective pharmacopoeia were slightly different for the peak ratio requirements of aglucone tested by HPLC(High Performance Liquid Chromatography).
USP stipulates that the ratio of kaempferol/quercetin is greater than 0.7, and the ratio of isorhamnetin/quercetin is greater than 0.1. The 2010 edition of the pharmacopoeia provided that the ratio of kaempferol/quercetin is 0.8~1.2, and the isorhamnetin/quercetin ratio is greater than 0.15. The BP and EP have no standards of peak ratio, they only regulates that the flavonoid glycoside content should between 22.0% ~ 27.0%, bilobalide content is between 2.6% ~ 3.2%, ginkgolides A, B, C content is between 2.8% ~ 3.4% and ginkgolic acid is no more than 5 PPM. Although the USP, the BP, EP and CP provided important rules in quality control of ginkgo biloba products, but these regulations can not provide a method to analyze the acid hydrolysis products. There are an exception, China Chamber Of Commerce Of Medicines & Health Products Importers & Exporters put forward, that rutin should be less than 4%, quercetin less than 0.5%, kaempferol no more than 0.5%, isorhamnetin no more than 0.2%, it also specifies the kaempferol/quercetin is no less than 0.7 in hydrolysis ginkgo biloba. The United States Pharmacopoeia increased the requirements of rutin and quercetin in the USP 37-2S redaction, but there were no rules for kaempferol and isorhamnetin.
Although these regulations have played a role in the standardization of ginkgo biloba in the market, they are not good enough to monitor the aglucone and other components of acid hydrolyzed process products. These have led to the proliferation of adulterated ginkgo. Ginkgo adulteration often has the following cases, the most common kind of adulteration is to add special original plant extract or a certain proportion of flavonoids and aglucone to reach the requirements of 24% flavonoids. Rutin, quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin are the most commonly used ingredients, and another adulteration uses other parts of ginkgo, such as root, peel or seed.
As mentioned above, using other flavonoids-rich raw materials is most commonly used in adulteration. Rutin and quercetin are rich in sophora pod and flower bud, in the meantime, they contain genistein and genistin, which can not found in ginkgo biloba extract. Therefore, if sophora pod and flower bud are used to adulterate, the two components of genistein and genistin will be detected in ginkgo biloba extract.

Ginkgo Biloba Leaf

Ginkgo Biloba Extract
2. High Performance Liquid Identification
2.1 Preparation of solution
Reference solution: Make the appropriate concentration solution of rutin, quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, genistein, genistin with methanol, which can be used as quantitative.Sample solution: The concentration of ginkgo biloba extract was 12mg/mL (methanol). The raw material of ginkgo biloba is 100mg/mL (methanol). Mixed 1g ginkgo leaf raw material powder with methanol, and made the suspension under ultrasonic 1 hour. The commercialized product is converted into 120mg extract. For the commercially available capsules and tablets, the sample weight was converted to 80mg flavonoid glycosides put into a 80ml volumetric flask and under ultrasonic 140 minutes with methanol. All samples are filtered by microfiltration membrane before testing.
The hydrolysis samples were prepared according to USP 37-NF 32, and the unhydrolyzed samples were analyzed in the same way.
The method is: Take gingko extract 0.3g to 250ml round bottom flask, add 78ml mixed solvent (methanol: hydrochloric acid: water = 50:20:8; V/V/V) backflow extraction 135 minutes (liquid becomes dark red), cool to room temperature, transfer to 100ml volumetric flask, add water to scale and shake well. Liquid phase analysis was carried out with liquid filted by microporous membrane.
2.2 Liquid phase condition
Agilent 1200 liquid chromatograph.
Luna C18-HST chromatographic column (2.7 mu m, 3 x 100mm)
Flow phase A: water;
Flow phase B: acetonitrile.
The flow rate is 1.0 ml/min.
Gradient elution: 0-1.5 min, 15-15% B; 3-4 min, 17-17% B; 7-14 min, 20-35% B;
Detection wavelength: 260nm, 360nm.
Sampling quantity: 1 μL
Balance each sample for 5min.
The relative retention time of quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin was 1.00 min, 1.17 min and 1.20 min.
2.3 Liquid chromatography results
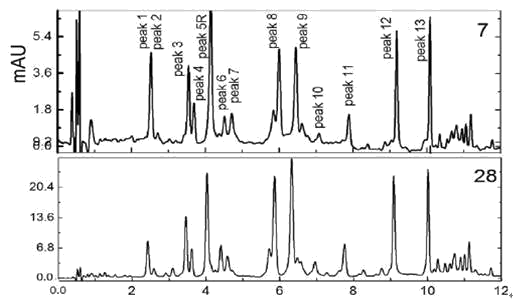
Picture 7 is ginkgo biloba raw material,Picture 28 is standardized ginkgo biloba extract

Pics 41 and 42 are ginkgo biloba extracts adulterated rutin, quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin
2.4 Results discussion
The following steps can be used to test whether ginkgo biloba extract is adulterated.
2.4.1. Test the ginkgo samples with non-hydrolysis method
(1) For the sample has 13 aglucone peaks, height of each peak is close to raw materials, and have no peak of genistin, genistein, quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin, then the sample is not adulterated;
(2) For the sample without flavonoid glycoside peak appeared, it first can be determined firstly that acid hydrolysis is used in this ginkgo products, but it needs to meet rutin no more than 4%, quercetin 0.5% or less,kaempferol 0.5% or less, isorhamnetin 0.2% or less, and no peak of genistein and genistin, then it is the true ginkgo biloba extract with acid hydrolysis process.
2.4.2. Test the ginkgo samples with acid hydrolysis method
(1) The peak ratio of kaempferol /quercetin and isorhamnetin /quercetin was used as the basis for judging.
(2)In the non-adulterated ginkgo biloba extract, the ratio of kaempferol /quercetin as 0.8 ~ 1.2, and the ratio of isorhamnetin /quercetin was greater than 0.15.
3.Thin Layer Identification
3.1 Thin layer identification conditions
Thin layer plate: Silicone G60, 10*10 cm.
Sample preparation: 1.0g sample with 10mL 70% ethanol, under ultrasonic 30 minutes.
Sample dose: 10 µL.
Expansion agent: Ethyl acetate:formic acid:glacial acetic acid:water =100:11:11:26, V/V/V/V.
Expansion span: 8cm.
Test:
First inject A reagent: diphenylboric acid - 2-amino-ethyl methyl alcohol solution (10g/L);
Then inject B reagent: polyethylene glycol 400 methanol solution (50g/L), slightly heated till to the spot is clear and detected in 366nm and visible light.
3.2 Thin Layer Chromatography
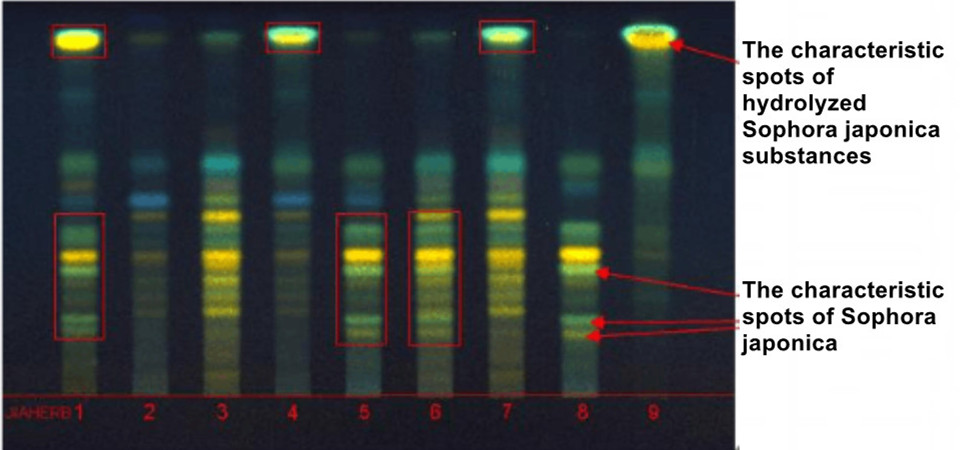
1. Gingko biloba extract (adulterated product); 2. Raw materials of ginkgo biloba leaf; 3. Ginkgo biloba standard extract (National Institute for Food and Drug Control); 4~7. Gingko biloba extract (adulterated product); 8.Sophora japonica extract; 9. Sophora japonica (acid hydrolysis)
3.3 Results discussion
From the thin layer atlas, it can be seen that the adulterated ginkgo biloba extract has obvious characteristic spots of hydrolyzed Sophora japonica substances or Sophora japonica.
4. Conclusion
There is a lot of adulteration in the market of ginkgo biloba extract. Liquid phase and thin layer methods can be used to identify the true and fake ginkgo biloba extract.
More details pls visit www.andybiotech.com, www.plusginkgo.com.





